The Importance of Air Velocity
If you have ever needed to choose a ceiling fan option, you will likely be familiar with performance metrics such as Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM) and Effective Coverage Area. These are common performance metrics most fan manufacturers provide. But have you ever considered how fast the air is moving? You know, the one that actually matters to you! That’s right, the one that most people overlook is air velocity; What is it and what does it really do? Let's break it down.
What is Air Velocity?
Air Velocity is measured in a few different ways. But here in North America, most people measure air velocity (speed, i.e. how fast the air is moving) in Feet Per Minute (FPM) and it refers to how quickly a fan can move air through a space. It is a key factor for the following:
- Basic Effective Temperature or “Windchill Effect”
- Air circulation
- HVAC efficiency
Let's explore each of them.
Basic Effective Temperature or “Windchill” Effect
You have more than likely experienced a lovely spring day, the thermometer may say 15°C (60° F) but due to the windchill, it will feel more like 8°C (46°F). Ceiling fans work on a similar principle-rather than changing the overall temperature; they make it feel cooling by increasing air velocity.
So, how does air velocity play into this? Well to calculate the basic effective temperature, you will need:
- 1. The actual room temperature (ex. 30°C/86°F) - Found along the vertical axes
- 2. The air velocity within the space
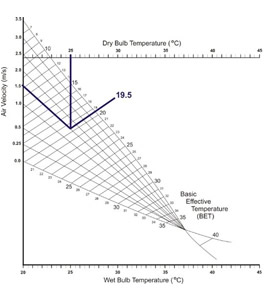
This graph, provided by the UK Health and Safety Board, illustrates how to determine the basic effective temperature in any given environment. To interpret it, begin by identifying the actual room temperature along the horizontal axis and trace a vertical line downward. Then, locate the corresponding FPM (feet per minute) value on the vertical axis. Using the diagonal lines on the chart, follow the line associated with that FPM value until it intersects with the vertical line drawn from the room temperature. The point where these two lines meet represents the basic effective temperature.
Air Circulation
Air velocity also impacts how well air circulates within a room. Picture two identical warehouses:
- Warehouse A has no fan and no air movement — the air is stagnant at 0 FPM, leading to stratification.
- Warehouse B is equipped with an Envira-North HVLS fan, pushing air at 497 FPM, resulting in continuous circulation and a de-stratified environment.
Even a minor increase to 50 FPM in Warehouse A wouldn’t compare to the performance in Warehouse B. Higher air velocity equals more effective and efficient air movement.
HVAC Efficiency
Air velocity affects more than just comfort; it has an impact on your HVAC system as well. Thanks to high air velocity and its effects on the perceived temperatures and air circulation, HVAC systems can be used less leading to:
- Lower energy bills
- Longer HVAC equipment lifespan
- Optimized HVAC usage
These can help any facility run more efficiently and effectively.
Final Thoughts
Air velocity is a vital metric when evaluating ceiling fans as it contributes to many important aspects:
- Comfortable temperatures (Perceived temperature)
- Eliminating the temperature differential (Air Circulation)
- Optimizing HVAC systems (HVAC Efficiency)
These can help any facility run more efficiently and effectively.
Other Articles You May Find Helpful
1. What is the Maximum Air Speed for a Fan & Why Not Faster - click here.
2. HVLS Fans vs. Traditional Ceiling Fans - click here.
3. Happier Clients by Controlling Thermal Comfort - click here.